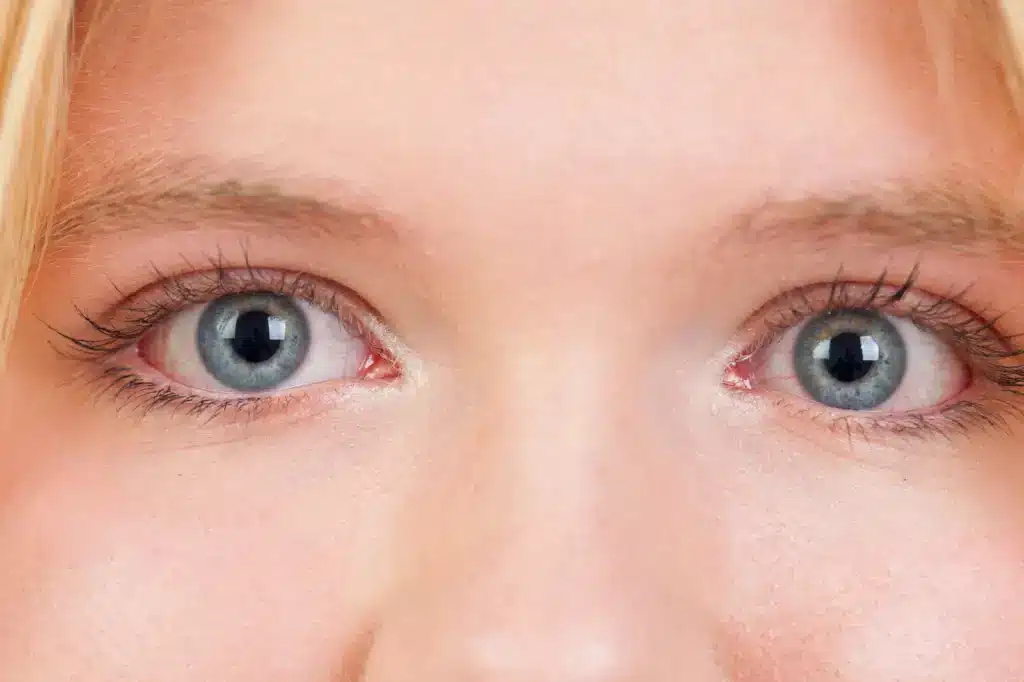
Dilated pupils can sometimes be a signal of drug use or serious medical conditions. Many different types of drugs, both legal and illegal, can cause your pupils to widen. Understanding the causes and effects of dilated pupils is important when it comes to recognizing potential substance abuse problems or other health issues.
What Dilated Pupils Can Signal
Dilated pupils can be an indicator of several different things.[1] However, you must realize that dilated pupils alone do not necessarily indicate a specific underlying cause.
- Drug use or intoxication: Many recreational and prescription drugs (stimulants, hallucinogens, and anticholinergics, among others) can cause pupil dilation as a side effect. Dilated pupils can be an indicator that you have recently used these types of substances.
- Excitement: The sympathetic nervous system, which controls your fight-or-flight response, can cause pupil dilation if you’re excited, aroused, or experiencing other strong emotions.
- Brain injury or neurological condition: Certain brain injuries, strokes, and neurological disorders can affect the neural pathways that control pupil size, resulting in abnormal pupil dilation.
- Medical conditions: Some medical conditions can cause asymmetrical pupil dilation. Certain eye injuries or eye diseases may also affect your pupil size.
- Lighting conditions: Pupils naturally dilate in low light conditions, allowing more light to enter the eye. Your pupils also constrict in bright light to protect your retina.
How Drugs Can Dilate Your Pupils
Drugs can dilate pupils by affecting the autonomic nervous system, which controls involuntary bodily functions.[2] How much pupil dilation you experience may vary depending on the drug and the dose. Here are a few ways drugs can cause pupil dilation:
- Stimulating your sympathetic nervous system: Drugs like amphetamines, cocaine, and methamphetamine stimulate the release of norepinephrine, a neurotransmitter that activates your sympathetic nervous system. This leads to the contraction of the iris muscles, which causes the pupils to dilate.
- Blocking parasympathetic nervous system activity: Drugs with anticholinergic effects, such as atropine, scopolamine, and some antihistamines, block the action of acetylcholine. Acetylcholine normally causes your pupil muscles to constrict. As a result, blocking its action leads to pupil dilation.
- Directly acting on the iris muscles: Some drugs, like mydriatic eye drops often used in eye exams, directly stimulate the iris muscles to contract. This causes your pupil dilation during the exam.
A List of Drugs Associated With Dilated Pupils
Several types of drugs, both legal and illicit, qualify as dilated pupil drugs, and many are controlled or dangerous substances, including:[3]
- Stimulants: Stimulant drugs can dilate the pupils. Amphetamines, such as Adderall, are prescribed for the treatment of ADHD and narcolepsy. Cocaine is a recreational drug that can also cause pupil dilation. Methamphetamine is another recreational drug that is a known dilated pupil drug.
- Hallucinogens: Hallucinogens are also known to dilate the pupils. LSD is a recreational drug that can cause pupil dilation, as well as psilocybin and mescaline.
- Anticholinergic drugs: Anticholinergic drugs can dilate the pupils, too. Atropine is used to dilate your pupils for eye exams and to treat certain neurological conditions. Scopolamine is used to treat motion sickness and postoperative nausea and vomiting, and it can also cause pupil dilation. Some antihistamines can dilate your pupils while treating allergies and insomnia.
- Opioid medications: Morphine is used to treat moderate to severe pain and can cause pupil dilation. Oxycodone is also used for pain management and can lead to pupil dilation. Hydromorphone, known by the brand name Dilaudid, is another opioid analgesic that can dilate your pupils.
- Miscellaneous drugs: Mydriatic eye drops are specifically used to dilate your pupils for eye exams. Certain antidepressants, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, can cause pupil dilation while being used to treat depression and anxiety.
Side Effects of Dilated Pupils
As a side effect itself, dilated pupils are also associated with its side effects that can increase discomfort, including:[4]
- Sensitivity to light: Dilated pupils will increase light sensitivity and discomfort in bright environments.
- Blurred vision: The widening of your pupils can cause the edges of your visual field to become blurred or distorted. This makes it more difficult to focus on close-up objects.
- Impaired night vision: The inability of your pupils to constrict can make it harder for you to see clearly in low-light conditions.
- Increased risk of eye injury: Dilated pupils expose your retina, making your eyes more vulnerable to damage from bright light or UV radiation.
- Difficulty with tasks requiring visual focus: Activities like reading, using a computer, or driving may be challenging due to the visual disturbances caused by your dilated pupils.
- Anxiousness or paranoia: In some cases, especially with drug-induced pupil dilation, you may experience feelings of anxiety and paranoia.
- Headaches or eye strain: Light sensitivity and blurred vision can lead to headaches or general eye strain and discomfort.
Gain Freedom From Substance Use Disorder
No one should have to battle substance abuse alone. Many treatment centers across America can provide the support and resources needed to overcome addiction and reclaim a happy, healthy life. If you find yourself in a battle with addiction, don’t hesitate to reach out and get the help you deserve.
FAQ’s
What medical conditions require the use of dilated pupil drugs?
Pupil-dilating drugs, also known as mydriatics, are commonly used for many different medical conditions and procedures.[5] Here are some of the primary reasons you might receive these drugs:
– Eye examinations: Dilating the pupils allows for a better view of the interior structures of the eye, like the retina and optic nerve. This is essential for diagnosing and monitoring conditions like retinal disorders, glaucoma, and macular degeneration.
– Assessment of ocular health: For general eye health evaluations or to detect early signs of eye diseases.
– Neuro-ophthalmic examinations: Dilated pupils can help assess the neurological health of the eye. This is important when diagnosing optic nerve disorders or brain tumors.
– Pre-surgical evaluation: Dilation may be necessary before certain eye surgeries to get a comprehensive view of the eye’s structures.
– Treatment of inflammatory conditions: In cases of uveitis or iritis, dilation helps to reduce pain and prevent complications.
Are there any long-term effects associated with repeated pupil dilation?
If you experience repeated pupil dilation, there could be some long-term effects you should be aware of.[6] Here are a few you might encounter:
– Light sensitivity: Frequent dilation can make your eyes more sensitive to light, which might persist even after the dilation effects wear off.
– Blurred vision: Repeated dilation can affect the focusing ability of your eye, causing persistent blurred vision.
– Increased intraocular pressure: Some dilating drugs can raise the pressure inside your eye, which could be problematic if you have glaucoma.
– Changes in accommodation: Accommodation is the ability of the eye to focus on near and distant objects. Frequent dilation could potentially affect this ability.
– Dry eyes: You might notice dryness or discomfort in your eyes after dilation, especially if you frequently dilate them.
– Potential for allergic reactions: Repeated exposure to dilating agents could increase the risk of allergic reactions or sensitivities over time.
Risk of retinal damage: Although rare, there is a potential risk of retinal damage with repeated use of certain dilating agents. This is also significant if you have an underlying retinal condition.
– Discomfort and sensitivity: Long-term repeated dilation might cause discomfort or increased sensitivity in your eyes. This could impact your daily activities and quality of life.
Can you reverse pupil dilation brought on by drug use?
If you’re dealing with pupil dilation caused by drug use, there’s no safe way to reverse the dilation. Most pupil-dilating drugs will wear off on their own after a certain period passes. The duration can vary depending on the drug that was used.
Sources
[1]American Academy of Ophthalmology. (n.d.). Dilated pupils: Causes for worry, concern, and treatment. Retrieved August 9, 2024, from https://www.aao.org/eye-health/tips-prevention/dilated-pupils-causes-worry-concerned-treatment
[2][3]Parker, L. (2023, October 4). Dilated pupils and drugs: Causes, effects, and treatment. Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/dilated-pupils-drugs#causes
[4][6]Goh, K., & Hsu, C. (2022). The impact of pupil dilation on visual performance and the effects of various substances. Journal of Clinical Ophthalmology, 16, 1245-1257. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9276640/
[5]Mayo Clinic. (2023, May 31). Eye dilation: What to know. https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/adult-health/expert-answers/eye-dilation/faq-20057882